Rolling Stock Scheduling Optimization

Project Objectives:
This primary goal of this collaboration between Swiss Federal Railways SBB and ETH Zürich is to create an algorithm for optimal rolling stock schedules.
Part I
During its first part, the project addresses the complexities of mid- and short-term rolling stock scheduling. In this setting, the yearly timetable of service trips and the regular rolling stock schedule is given, but due to unforeseen events such as construction work or rolling stock malfunctions, the regular schedule is disrupted and became infeasible. The objective is to swiftly address the issues and to create a new rolling stock schedule that seamlessly fit into the long-term plan while satisfying all maintenance regulations and other side-constraints. The objective is to serve all trips with the limited rolling stock units given by the general schedule while minimizing the costs caused by unnecessary dead-head-trips without violating the maintenance regulations.
Part II
For the second part of the project, the optimization algorithm is applied to futuristic scenarios anticipating the mobility landscape of 2050. The key objectives of this part are to minimize rolling stock units and the travel distance of dead-head-trips, while meeting the dynamic passenger demand and still satisfying the maintenance regulations.
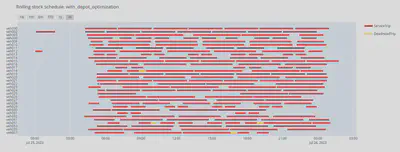
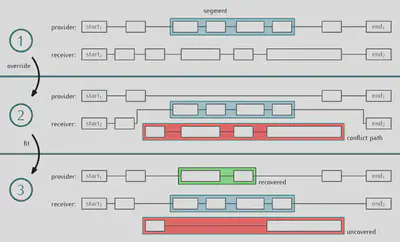
Optimization Approach:
Integrating state-of-the-art methodologies, our optimization approach combines local-search meta-heuristics and classic minimum-cost flow algorithms. Local search improves rolling stock schedules through small, local modifications, such as exchanging adjusting train compositions, or exchanging a sequence of service trips to another rolling stock vehicle. Simultaneously, the optimality of classic minimum-cost flow algorithms ensures minimal overall costs.
Technological Stack:
Since mid- and short-term rescheduling of rolling stock units might be time-critically, and for meta-heuristics there is always a tradeoff between objective quality and running time, we decided to aim for a high performance approach utilizing a multicore architecture.
Rust: The core programming language, providing high performance, reliability, and enabling parallelism for efficient utilization of computational resources.
Docker: Used for containerization, ensuring a consistent and isolated environment for seamless deployment.
HTTP Server: Facilitating communication and interaction with the optimization algorithm, ensuring strict and reliable interfaces for efficient integration into the SBB framework.
Project Leadership
I am in charge as the primary project lead, responsible for all coding efforts in Rust and implementing state-of-the-art algorithms, as well as, the requirement engineering and overall exchange with our partners at SBB. In addition, I supervise student projects experimenting with further algorithmic approaches for rolling stock scheduling.