Fast Same-Day Delivery Optimization
Project Objectives:
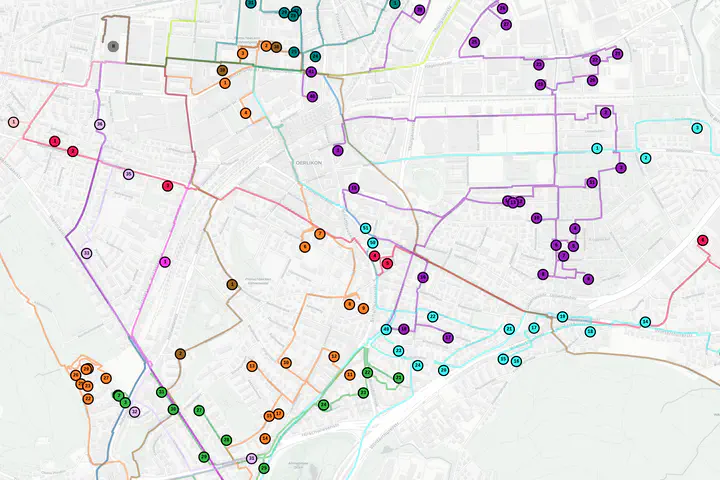
The collaboration between Swiss Post (and its subsidiary company Notime) and ETH Zürich is to optimize same-day shipment delivery in Zurich, Bern and eight other Swiss cities. The primary objectives consist of efficiently scheduling shipments to driver tours while minimizing the number of late shipments, the driver costs and the total driving distance.
All shipments are sorted at one central hub, each of them have an individual delivery location a specified time windows for drop-off. Drivers come with different shifts and experience levels. Some drivers might only work half of a day, but be ready-on-demand for the other half (stand-by-time). In addition, vehicles have a capacity on how many shipments can be transported. Notably, the algorithm is designed to be exceptionally fast, ensuring real-time optimization for the same-day-delivery for e-commerce (Digitec) and short-term grocery delivery (Migros).
Key Features:
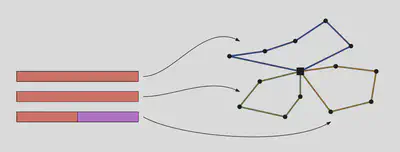
Optimization Algorithm: The sophisticated optimization algorithm is written in Scala 3 and consists of local-search meta-heuristics (variable neighborhood search, tabu search) utilizing optimal hierarchical matching algorithms and a state-of-the-art traveling salesman subroutine.
Constraints: Shipments originate from a central hub, and the algorithm efficiently distribute the shipments to driver tours for delivery within specified time windows. It takes vehicle capacities, different driver profiles (shift, experience level) as well as drop-off times into account.
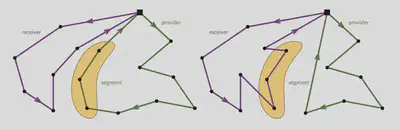
Asymmetric Travel Times: The algorithm handles asymmetric travel times, caused by one-way roads and varying terrains. This feature is particularly crucial for efficient bicycle-based deliveries in hilly areas.
Objective: The objective is to deliver all shipments within their time limits while minimizing overall delivery costs, which are caused by drivers’ overtime or used stand-by-time, and the total driving distance.
Robustness: The provided driving times are estimates given by a travel time provider. As the real experienced driving times will differ from these estimates and unforeseen delays might always happen, the schedule has to be robust. We designed our algorithm to be resilient against these uncertainties.
Technological Stack:
In order to fit seamlessly into the Notime framework, we used the following tool set:
- Scala 3: An object-orientated and functional programming language running on a Java virtual machine.
- Docker: Containerization, providing a consistent and isolated environment for seamless deployment.
- HTTP Server: For efficient integration into the Notime framework.
Project Leadership:
I led this collaboration for two years, taking charge of project management, strategy, and development. As a key contributor, my role also involves the design, development, and implementation of the optimization algorithm, as well as the communication and requirement engineering with Notime. I successfully introduced several agile concepts for an improved coordination within the small team.